1. Understanding Multi-factor Authentication

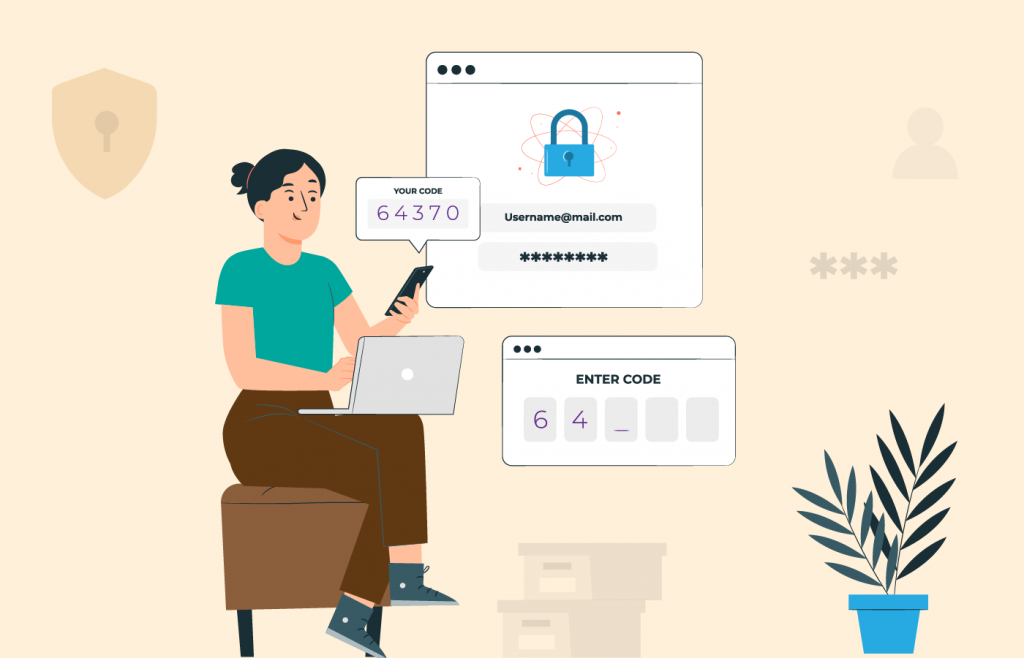
Multi-factor authentication is a security mechanism that requires users to verify their identities using at least two of three main components.
- Something you know (like a password)
- Something you have (like a physical token or a smartphone)
- Something you are (like a fingerprint or other biometric data)
MFA works by requiring multiple layers of verification, making it significantly harder for unauthorized individuals to gain access. In contrast to single-factor authentication (a password alone, for instance), it provides an extra line of defense against cyber threats.
2. Benefits of Implementing MFA in the Workplace
The advantages of using MFA are numerous. Here are a few of them:
2.1 Reducing the risk of unauthorized access
MFA's primary purpose is to prevent unauthorized access to sensitive data. By requiring more than one piece of evidence for authenticating users, MFA greatly reduces the chance of unauthorized access. According to a Symantec study, MFA could prevent approximately 80% of data breaches.
2.2 Protecting sensitive data
Data violations can profoundly harm businesses, causing damage to their reputation and inducing severe financial fallout. According to the Ponemon Institute, the average total expense of data breaches in 2020 amounted to a whopping $3.86 million. Nevertheless, organizations can notably curtail such risks and keep expenses in check by embedding multi-factor authentication (MFA) into their systems and procedures.
2.3 Regulatory compliance
MFA can also help your organization comply with industry regulations. For example, industries such as healthcare (HIPAA) and finance (PCI DSS) require robust security measures, including MFA, to protect sensitive data.
2.4 Deterring phishing and other threats
Finally, MFA serves as an effective deterrent against common security threats like phishing. According to Verizon's 2020 Data Breach Investigations Report, 22% of breaches in 2020 involved phishing. MFA can considerably curb the risk of these types of assaults by supplying an extra security tier, even when the primary credentials are breached.
3. Integrating Mobile Credentials into MFA Systems

Incorporating mobile credentials into your MFA systems can enhance security even further. These credentials are held on a user's smartphone, providing an extra layer of verification.
Mobile credentials come with several benefits, including convenience (most people have their smartphones handy), reduced reliance on physical tokens (which can be lost or stolen), and enhanced security through device-based biometric authentication.
The majority of people always have their smartphones with them, which makes it a pragmatic choice for a secondary or tertiary authentication method. Users are generally more likely to remember to bring their phones than a physical token or card, reducing the chance of being locked out due to a forgotten credential.
Furthermore, physical tokens can be lost, stolen, or simply forgotten. By shifting authentication to a device that's typically always with the user, organizations can minimize these risks. Additionally, replacing lost tokens can be costly and time-consuming for businesses, another issue that mobile credentials help to avoid.
In the workplace, mobile access control for credential verification can be implemented in various scenarios, from building entry and Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) to cloud applications.
4. Best Practices for Implementing MFA in the Workplace

When deploying MFA, it's crucial to pick a solution that aligns with your corporation's requirements. Reflect on factors such as user-friendliness, scalability, and compatibility with the existing infrastructure.
The implementation of multi-factor authentication (MFA) in the work environment can substantially uplift your organization's security stature. However, to ensure its effectiveness, here are some best practices to follow:
4.1 Selecting an MFA solution
To implement an effective MFA solution, it's crucial to evaluate your organization's unique needs. Some key factors to consider include:
- Ease of use: It should be user-friendly to encourage employee adoption. According to a 2019 Ponemon Institute study, 51% of employees see security as a hindrance to productivity. Choosing an easy-to-use solution can mitigate this perception.
- Scalability: The chosen MFA solution should scale with your organization. As per Gartner's prediction, by 2022, 60% of large and global business, and 90% of midsize enterprises, will continue using passwordless solutions in over a half of use cases.
- Compatibility: Ensure the MFA solution is compatible with your existing systems. Incompatibility can lead to significant productivity losses.
4.2 User education and training
Employees play a crucial role in ensuring the success of MFA implementation. It's essential that they understand its value and how to properly employ it:
- Education: Inform them about the relevance of MFA in securing sensitive data. In 2019, 62% of businesses reported experiencing phishing and social engineering attacks, which MFA can help mitigate.
- Training: Train them to handle MFA mechanisms. Regular drills can help them become familiar with the process.
4.3 Addressing Potential Challenges
Implementing MFA comes with potential challenges, but they can be managed effectively with proper planning.
- Balancing security and usability: It's essential to strike a balance between security and usability. A robust MFA solution that's hard to use can deter employees and reduce productivity.
- Managing lost or stolen devices: Establish policies for managing lost or stolen devices used in the MFA process, like mobile phones. This might include a fast-track procedure for revoking access and re-establishing it on a new device.
- Temporary or emergency access: Have emergency plans when usual MFA methods do not work. This could involve backup codes or secondary authentication methods.
By following these best practices, you can effectively leverage the benefits of MFA and strengthen your organization's security stance.
5. Real-world Examples of MFA in Action

Numerous organizations have successfully improved their workplace security with MFA. To illustrate this point, here are a few world-renowned organizations that have demonstrated the importance of cybersecurity by implementing multi-factor authentication (MFA) or similar measures.
- Google - Google is renowned for its first-rate security protocols - they even created an MFA tool called Google Authenticator which adds an extra layer of protection to user accounts.
- Microsoft - Microsoft offers MFA as part of its Azure Active Directory and Microsoft 365 products, encouraging users to take advantage of it in order to secure data and protect sensitive information more effectively.
- Amazon - As one of the largest e-commerce and cloud computing companies, Amazon places a high priority on security. They have implemented MFA for various services, such as AWS (Amazon Web Services), to safeguard customer data and prevent unauthorized access.
- Cisco - Cisco Systems, a multinational technology conglomerate, has implemented MFA to strengthen its security posture. By using MFA, they ensure that only authorized individuals can access their internal systems and sensitive information.
- IBM - IBM, a giant in technology and consulting, advocates for the use of MFA to guarantee maximum security for both its internal systems and solutions provided to clients.
- Dropbox - Dropbox, a beloved cloud storage and collaboration provider, offers multi-factor authentication as an additional layer of protection to users' accounts and data.
- Salesforce - Salesforce's CRM platform is equipped with powerful MFA capabilities, allowing customers' sensitive information to be protected within a strongly secured environment.
- PayPal - PayPal also uses MFA for maximum account security and safe online payment transactions too!
- Twitter - Twitter also incorporates this extra layer of verification - keeping user accounts safe from unauthorized access attempts. Users can enable MFA through their account settings.
- LinkedIn - LinkedIn, a professional networking platform, offers MFA to its users as an optional security feature to protect their accounts and personal information.
In Summary
Multi-factor authentication is a critical tool in bolstering workplace security. By integrating mobile credentials into MFA systems, businesses can add another layer of protection.
However, it's important to remember that successful MFA implementation also requires user education and training. By adopting these measures, companies can notably lessen the threat of cyber attacks and secure their confidential data and systems.
 Interested in Virtual Team Building Events?
Interested in Virtual Team Building Events?